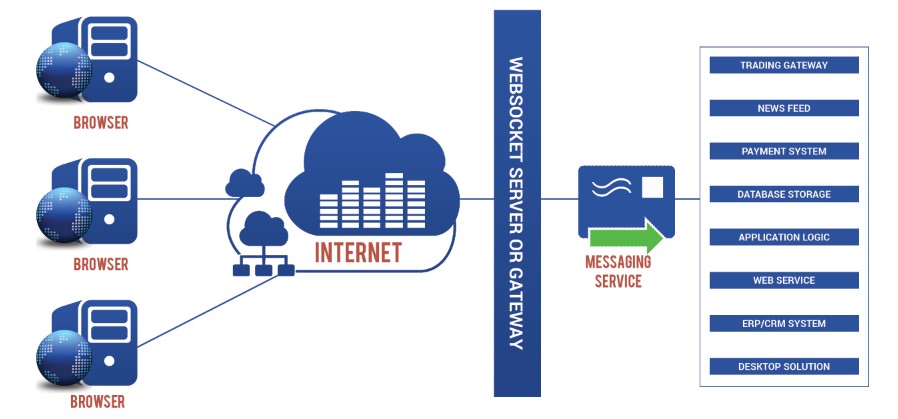
How To Choose a Cloud Service?
It is an undeniable truth that Information Technology has transformed the way business is done. The enticing features inherent to the cloud concept such as storage and processing of data in third party data centres, access to various services at convenient prices and adequate sharing of necessary resources etc. have ensured its widespread acceptance and dependence across industries.
Choosing a cloud computing service can be a simple process if one knows what he wants, knows what to expect and understands business requirements. Primarily, there are three types of cloud computing service providers that provide unique cloud services:
Software as a service (SaaS)-
These are service providers that offer software as services. For example: Google Docs, Microsoft Office 365 etc. SAAS eliminates the need to install and run applications on individual computers. Though a few plugins might be required, SAAS applications can be run directly from a web browser without any downloads or installations.
Platform as a service (PaaS)-
PaaS is primarily a framework for developers to build, develop and customize applications. The development, functioning and testing of applications made using PAAS is hassle free, fast and economic.
Infrastructure as a service (IaaS)-
Iaas provides a virtual environment for access to the computing resource. The clients subscribing to this form of cloud computing are given access to virtualised components so that they could build their own IT platforms.
All these services are cost efficient and time saving as they save clients the trouble of setting everything right from servers to hardware up from scratch. This means that the memory required by a website to respond to a sudden increase in end users can be doubled within minutes, given the efficiency and scalability of these services. Most of these services can be availed on a pay-per-hour basis that is exclusive to each server, role or process.
Deployment Models: Which one to choose?
There are choices to make when it comes to adopting a cloud solution. The deployment of different models depends on the needs of each company. Some of the most effective cloud services available are as follows:
Windows Azure:
Windows Azure, which functions on the PaaS platform and supplies as well as manages the operating system, is a great choice to opt for if a specialized OS is not required in the building of applications. This means that one can devote complete attention to the building, deployment and the management of cloud applications without having to worry about OS updates and patches. Primarily, Azure offers three main roles:
- Web Role: This is an Internet Information Services 7 Windows Azure supplied OS that enables the development of applications using web technologies such as ASP.NET, PHP and Node.JS
- Worker Role: This Windows Azure supplied OS enables the hosting of applications such as Apache, Tomcat amongst several others and runs arbitrary code.
- Virtual Machine Code: By uploading a Windows Server 2008 R2 (Enterprise or Standard) VHD image, the customer supplies the OS in this service. This role, which is presently in Beta, renders the customer responsible for updating the OS. Applications can be built on Windows Azure using any language, tool or framework.Microsoft offers a three month free trial of Azure, which is adequate time enough for professionals to become well-versed with it. The service can be bought on a pay-as-you-go basis or a six month commitment for customized, reduced pricing.
Amazon’s AWS:
Amazon Web Services (AWS Cloud) from Amazon that offers raw infrastructure to enable the functioning of any OS a customer’s applications might require. Despite offering OS control, Amazon Elastic lacks automated patching. Import of supported virtual machine images, creation of instances based on numerous Linux and Windows OSs is made possible. The service can be bought on an hourly rate basis, a one-time fee basis which entails a discounted hourly rate with a commitment of one or three years and on the basis of bidding. Following are best compute services in Amazon Web Services :
- Auto Scaling:Auto Scaling helps you maintain application availability and allows you to
scale your Amazon EC2 capacity up or down automatically according to conditions you define. - Amazon RDS: This makes easier to set up, operate, and scale a relational database in the cloud. It provides cost-efficient, resizeable capacity while managing time-consuming database management tasks, freeing up to focus on applications.
- Elastic Load Balancer:This automatically distributes incoming application traffic across multiple Amazon EC2 instances in the cloud.
OpenStack:
OpenStack is a popular and rapidly developing cloud platform for the creation of IaaS (infrastructure as a service) platforms. It is jointly founded by Rackspace and NASA and is supported by other multiple established vendors including HP, IBM, Rackspace, Dell and Red Hat. It is a platform for creating and managing large groups of virtual private servers in cloud computing environment.
It controls large pools of compute storage and networking resources throughout a datacenter all managed through a dashboard that gives administrators control while empowering users to provision resources through a web interface. Many have deployed Openstack clouds to achieve control,business agility and cost savings without the licensing fees and terms of proprietary software. Its massive industry support, AWS compatibility, security, and powerful dashboard has made it highly competitive.
Rackspace Cloud Hosting:
Is a service that provides raw infrastructure with control over the OS. Rackspace, unlike other Iaas providers, does not allow the upload of a customer’s own virtual machines. Rather, either the Windows or the Linux versions, which are supported by the company must be chosen.
Rackspace offers numerous server sizes and charges a per hour fee for each server.
Rackspace, unlike others, does not let one stop the per-hour charges by halting instances. If one wants to be in possession of an idled server without being charged for it, the back-up must be done for the image (Which again incurs charges from Rackspace) and the server must be deleted from the account. The server can be added back anytime later.
The company presently does not offer a free trial. However, an account can be created for free to gain access to the administrative portal which gives a better understanding of the service’s functioning. Charges would only be incurred if any instances are created or other resources are used.